Parathyroid Hormone Pth Has Which Effects on the Kidney
The main target tissue of PTH is the kidney where PTH has three effects. For example if the blood level of calcium becomes low the parathyroid glands will release more PTH.

Direct And Indirect Effects Of Parathyroid Hormone On The Download Scientific Diagram
PTH is secreted in response to.

. Another effect of parathyroid hormone on the kidney is to stimulate loss of phosphate ions in urine. If a person is on dialysis and their intact PTH level is less than 100 pgml this is known as dynamic bone disease also known as low bone turnover. More PTH will cause the bones to release calcium and the blood calcium level will.
Parathyroid hormone enables the production of active vitamin D calcitriol in your kidneys. Because 2 HPT is a compensatory. What effect does PTH have on the kidneys.
Receptor CaR in the parathyroid gland and skeletal resistance to the calcemic effect of PTH. Question Parathyroid hormone PTH has which effects on the kidney. This may occur if the parathyroid glands become overly suppressed with vitamin D medication such as Zemplar or Hectorol.
Parathyroid hormone signals your small intestine to absorb more calcium from the food you eat. Caused by surgical removal of parathyroid gland surgical trauma or radiation. If your kidneys work poorly usable vitamin D may decline and calcium levels drop causing parathyroid hormone levels to go up.
A reduction in calcitriol also contributes to a reduction in intestinal calcium absorption. In the absence of PTH action the renal mechanisms transporting calcium and phosphate reabsorption deregulate resulting in hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia. This in turn leads to high levels of calcium meaning HPT can result in calcium kidney stones that hinder kidney function.
Disturbances in mineral metabolism are common among older adults and may adversely impact cardiovascular health. In the kidney parathyroid hormone PTH blocks reabsorption of phosphate in the proximal tubule while promoting calcium reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle distal tubule and collecting tubule. Most of the physiologic calcium reabsorption in the nephron takes place in the proximal convoluted tubule and additionally at.
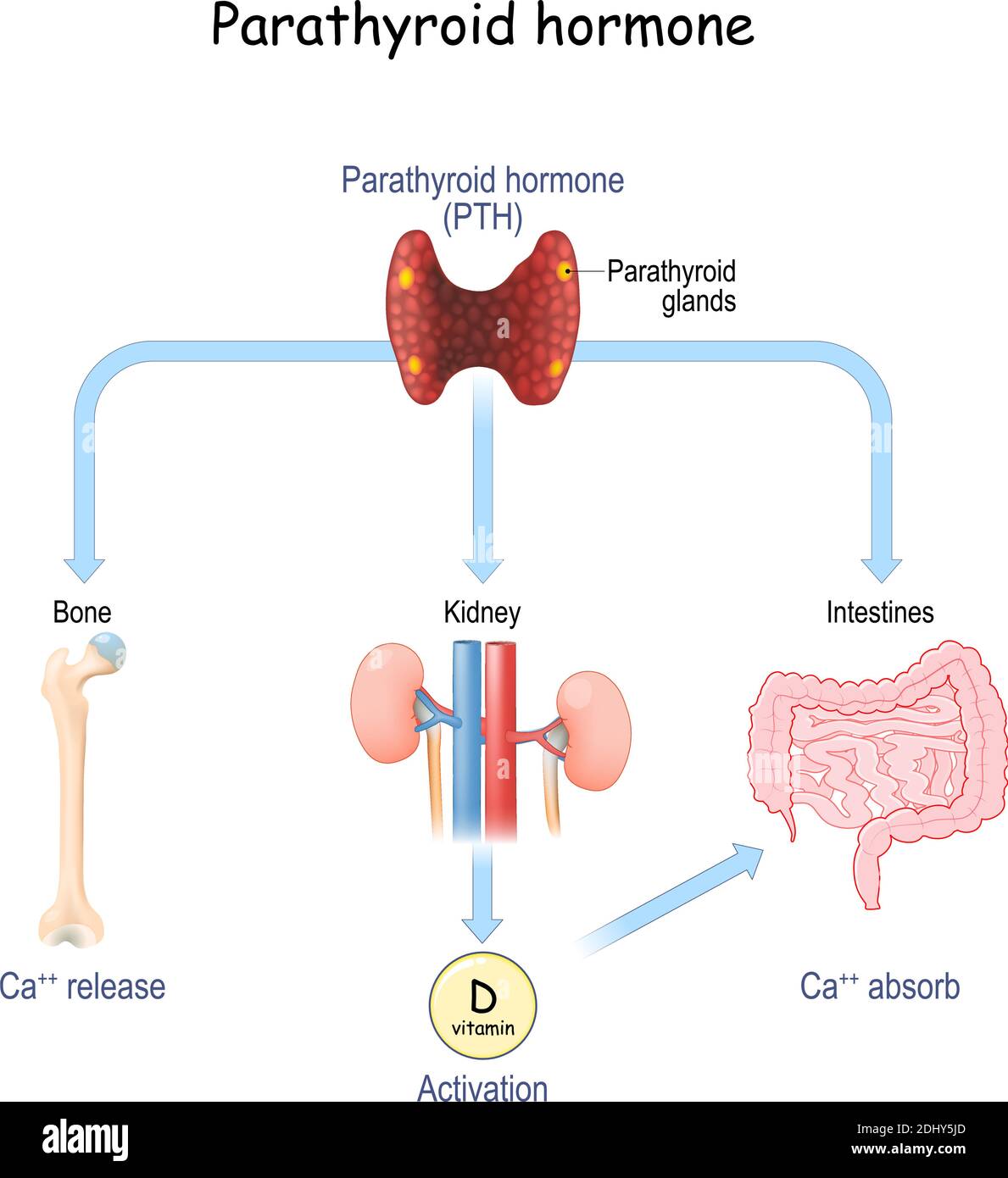
It does this through its actions on the kidneys bones and intestine. Addition information on how parathyroid hormone and vitamin D control calcium balance can be found in the section Endocrine Control of Calcium Homeostasis. And third to increase the excretion of phosphate.
PTH influences bone remodeling which is an ongoing process in which bone tissue is alternately resorbed and rebuilt over time. Hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia are the pathognomonic biochemical features of hypoparathyroidism and result directly from lack of parathyroid hormone PTH action on the kidney. In the kidney parathyroid hormone PTH blocks reabsorption of phosphate in the proximal tubule while promoting calcium reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle distal tubule and collecting tubule.
Effects of PTH on the Kidneys. PTH and the metabolites of vitamin D have different effects in the kidneys but it seems that PTH has a more power on calcium and phosphate regulation via the kidneys Bullock et al. Chronic kidney failure is the most common cause of secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Parathyroid hormone influences the net balance of how much calcium and phosphorus are removed and how much is retained during that process 3. Parathyroid hormone PTH promotes absorption of calcium from the bone in 2 ways. Both vitamin D and PTH hormone act physiologically on the endothelium heart and other vascular structures.
1 2 Older age is associated with lower circulating concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D 25-OHD impaired vitamin D activation within the kidney and a rise in serum parathyroid hormone PTH concentrations. When PTH is low more calcium is eliminated in the urine decreasing the calcium concentration in blood 3. Bones parathyroid hormone stimulates the release of calcium from large calcium stores in the bones into the bloodstream.
Stimulation of calcium reabsorption and phosphate excretion. The release of PTH is turned on and off depending on the levels of calcium in your blood. First to increase the reabsorption of calcium from urine.
Effects of Vitamin D Cardiovascular System. Control of Parathyroid Hormone Secretion. Second to increase the expression of the enzyme 1α-hydroxylase which activates vitamin D Fig.
Some medical treatments such as vitamin D bisphosphonates and cinacalcet will lower PTH levels. Parathyroid hormone regulates calcium levels in the blood largely by increasing the levels when they are too low. Parathyroid hormone PTH promotes absorption of calcium from the bone in 2 ways.
Parathyroid hormone also called PTH controls how much calcium is in your blood and within your bones. Parathyroid hormone also called parathormone or parathyrin is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone kidney and intestine. Caused by PTH hyposecretion and tisssue resistance to PTH PTH-dependent Hypocalcemia.
Sep 18 2016 Parathyroid hormone metabolism and signaling in health and chronic kidney disease Circulating parathyroid hormone PTH shows a complex relationship with hard outcomes in subjects with chronic kidney disease CKD. Increases renal reabsorption of calcium. Keeping this in view what is the effect of PTH on the kidneys.
PTH also signals your kidneys to retain calcium in your body rather than flushing it out through your urine. This increases bone destruction and. As kidney function declines so does phosphorus excretion thus causing plasma phosphorus levels to rise while plasma calcium and calcitriol levels decrease.
At the kidneys parathyroid hormone has 3 functions in increasing serum calcium levels. Biologic Effects Of Parathyroid Hormone PTH regulates serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations through receptors on bone intestine and kidney Direct GI effect of PTH on intestinal calcium or phosphate absorption is weak PTH stimulates renal production of 125-D absorption of Ca and phos. Parathyroid hormone has two target tissues.
When PTH is high the kidneys retain more calcium. As the kidney function deteriorates the PTH level gradually increases. In some people with long-term end.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism 2 HPT is the elevation of parathyroid hormone PTH in response to hypocalcemia induced by phosphate retention and reduced calcitriol synthesis as a consequence of reduced renal function10 In 2 HPT all the parathyroid glands become enlarged owing to parathyroid hyperplasia. HPT causes enlargement of one or more parathyroids which can lead to an above-average release of PTH in the body. PTH increases serum calcium by increasing bone resorption of calcium into blood this requires vitamin D.
Moreover intervention studies directly targeting PTH failed to yield unequivocal results.

Hyporesponsiveness Or Resistance To The Action Of Parathyroid Hormone In Chronic Kidney Disease Nefrologia
Parathyroid Hormone And Calcium Metabolism Parathormone Or Parathyrin Pth That Regulates Serum Calcium Through Its Effects On Bone Kidney Stock Vector Image Art Alamy

Normal Calcium And Phosphorus Homeostasis Pth Parathyroid Hormone Fgf 23 Fibroblasts Growth Factor 23 Parath Healthy Bones Osteoporosis Causes Bone Density
No comments for "Parathyroid Hormone Pth Has Which Effects on the Kidney"
Post a Comment